Physical Address
Timertau, Pr. Respubliki 19, kv 10
Physical Address
Timertau, Pr. Respubliki 19, kv 10

In recent times, the deactivation of license keys has garnered increased attention due to the profound repercussions it has on user access to various applications. When a key is rendered invalid, users may experience activation failure, leading to unforeseen difficulties in utilizing the software they rely on daily. This situation can compel individuals and organizations to reassess their strategies for managing software licenses.
One of the significant risks associated with license deactivation is the potential for system lockout. Users who fail to validate their licenses promptly may find themselves unable to access vital tools and features. Such lockouts not only disrupt productivity but also hinder ongoing projects, thus affecting overall performance.
Furthermore, understanding the factors that contribute to license suspension is essential for minimizing adverse outcomes. Organizations need to be proactive in monitoring their licenses to avoid falling victim to unexpected license deactivations, which can lead to both operational challenges and financial losses. Instances of unauthorized usage or failure to comply with licensing agreements can amplify these risks, creating a precarious situation for software management.
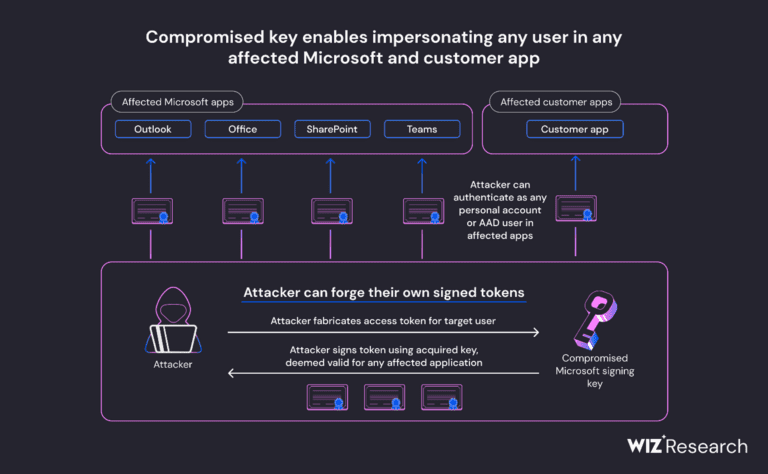
In the realm of software licensing, the deactivation of licenses through key management procedures can lead to significant challenges for users. One of the primary concerns is activation failure, which occurs when an application cannot verify the legitimacy of its license. This issue can arise from various factors, including unauthorized access or alterations made to the original license key.
When a key is invalidated, ongoing access to associated products may be lost. Users could experience license deactivation, resulting in the inability to utilize purchased software. This situation not only frustrates consumers but also raises risks associated with unexpected disruptions in productivity, especially for businesses relying on specific applications for daily operations.
Moreover, the consequences of deactivation can extend to financial implications. Users may find themselves ineligible for refunds or exchanges, putting further strain on their investments. The potential for an unexpected loss of access without recourse highlights the importance of maintaining secure and verifiable licensing agreements.
Organizations should consider implementing preventive measures to mitigate the risks attached to license management. Regular audits of software usage, education on how to identify and report suspicious activities, and understanding the protocols for key validation are essential steps to ensure continued access and functionality.
In summary, awareness of the procedures surrounding license management is crucial for end-users. Being informed can help avoid complications associated with activation failures and reduce the likelihood of encountering obstacles stemming from license deactivation.
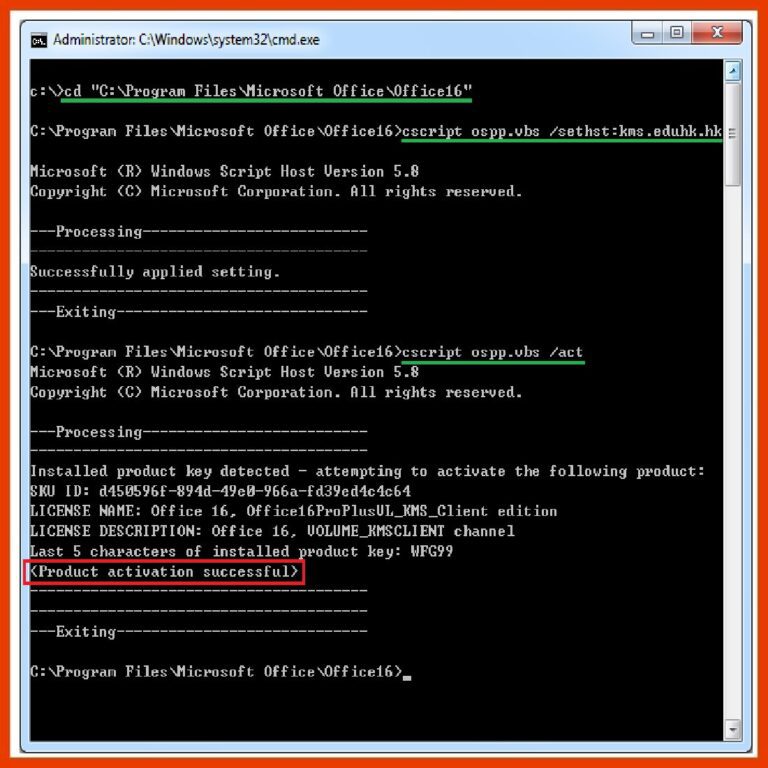
The deactivation of licenses can lead to significant issues for users, directly affecting the functionality of applications. One of the immediate repercussions is activation failure, which means that previously functional software may no longer run as intended. This can disrupt daily tasks and workflows, particularly for businesses relying on these tools.
Risks associated with this scenario are manifold. Users may experience downtime, loss of productivity, and potential data access issues. In addition, the inability to activate the software can result in significant time wasted on troubleshooting or seeking support.
Another critical aspect to consider is the financial implications. Once a license is deactivated, users might face no refund policies. This means that investments made in purchasing the license could lead to loss without recourse, compounding frustrations. For many, this represents an unfair loss, as they have already paid for services that they can no longer access.
Ultimately, the consequences of license deactivation extend beyond mere inconvenience. It is essential for users to remain aware of these risks and ensure they have access to necessary applications to maintain their operational capabilities.
The cancellation of authorization codes can lead to significant challenges for users and organizations alike. Understanding these implications is essential for anyone dealing with licensing and product activation.
When a code is invalidated, several consequences arise:
| Consequence | Description |
|---|---|
| No Refund | Users may be left without financial recourse after purchasing a deactivated license. |
| System Lockout | Access to software can be revoked, causing operational delays. |
| Activation Failure | Software may fail to generate necessary licenses for continued use. |
| Risks | Potential security threats arise from using unlicensed products. |
In conclusion, understanding the ramifications of license cancellation is critical for managing software resources effectively. Organizations should assess their licensing strategies regularly to mitigate these risks and maintain operational efficiency.
For more information on software licensing management, you can visit Microsoft Licensing.
Businesses must proactively address potential disruptions caused by license deactivation and related access problems. By implementing strategic measures, organizations can minimize risks associated with activation failure and system lockout events.
Here are some best practices to ensure continuity:
By integrating these practices, organizations can effectively reduce the risks associated with license deactivation and maintain smooth operational workflows, ultimately safeguarding productivity and minimizing disruptions.
In today’s environment, maintaining access to applications can be difficult due to various factors, including license management and the potential for system lockout. To address these issues, organizations can implement several technical strategies that mitigate risks associated with license deactivation and ensure smooth operations.
Using specialized tools for license management can streamline the process and reduce the chances of unexpected lockout. These systems typically offer:
Having backup licenses available can prevent disruptions. In cases where primary licenses become invalid or are deactivated:
Conducting regular audits helps ensure compliance and identify potential issues before they affect users. Steps to follow include:
Organizations should develop and communicate clear policies regarding license usage. This includes:
Transitioning to cloud-based applications can alleviate some challenges related to licensing. Benefits include:
Having a well-defined contingency plan can limit risks associated with potential license failures:
By considering these technical solutions, organizations can better manage the risks associated with license deactivation and system lockout, ultimately ensuring continued access and operational efficiency while minimizing financial loss such as no refund scenarios.
The sudden deactivation of licenses can lead to significant difficulties for users who rely on specific applications. When a product key is annulled, the immediate consequences may include system lockout and activation failure, which can interrupt critical workflows. Users often find themselves scrambling for solutions.
Many report that when their access is suddenly revoked, they experience frustration and confusion. Licensing issues can result in a no refund policy that leaves users feeling stranded without recourse. This lack of support can exacerbate feelings of helplessness, especially for those in urgent need of the software’s functionalities.
To mitigate these challenges, users have devised various strategies:
Real-time adaptation can involve a steep learning curve. Some users discover that understanding their licensing agreements better can help prevent future disruptions. Being informed about the signs of potential license deactivation enables individuals to act swiftly before total access is lost.
In summary, dealing with the abrupt cancellation of activation codes highlights the importance of preparedness and community engagement. Users navigating these issues often find value in sharing knowledge and supporting one another through the process.
For further reading on software licensing policies, visit the official site of the Electronic Frontier Foundation at https://www.eff.org.
The future of digital tools is approaching a critical juncture where enhanced license deactivation measures are being implemented. These policies are designed to mitigate risks associated with unauthorized access and ensure system integrity. As these regulations become stricter, users will face significant changes that may influence their experience and access to applications.
One of the most pressing concerns is the potential for system lockout. When a license is deactivated, users may find themselves unable to utilize essential programs, leading to interruptions in workflow and productivity. This phenomenon can be particularly disruptive in professional environments, where access to key tools is paramount for day-to-day operations.
The risks associated with such a shift include not only immediate access issues but also longer-term implications for users. For instance, frequent activation failures may occur when software attempts to verify its licensing status, resulting in frustration and downtime. Companies must be vigilant in tracking their licenses to avoid unexpected disruptions caused by these deactivations.
Moreover, license deactivation can significantly impact businesses that rely on subscription-based models. As these practices become more rigorous, organizations may need to invest in better license management solutions. This shift will demand both financial resources and strategic planning to ensure uninterrupted access while maintaining compliance with ever-tightening regulations.
In conclusion, the direction towards stringent license deactivation policies signifies a much-needed evolution in software management. Users must adapt to these changes, recognizing the risks involved while seeking to establish more reliable access to the tools they depend on. Preparation and awareness will be key in navigating this transition successfully.