Physical Address
Timertau, Pr. Respubliki 19, kv 10
Physical Address
Timertau, Pr. Respubliki 19, kv 10

The choice to operate a non-activated version of an operating system can lead to a series of significant limitations that users must consider. One major aspect is the customization restrictions that come with such a setup. Users often find themselves unable to personalize their interface or software features to suit their preferences, which can hinder productivity and overall user experience.
In addition to the limitations on customization, users may face various functional limits. Features that are typically available in activated software could be restricted, impacting the ability to perform specific tasks efficiently. This lack of functionality often extends to the absence of critical updates, which are vital for maintaining system security and stability.
Another notable inconvenience involves recurring notification prompts reminding the user of the unactivated status. These prompts can be distracting and may interrupt workflow, leading to frustration. Understanding these challenges is crucial for those considering whether to use a non-activated system, as it helps in weighing the immediate benefits against potential drawbacks in usability and efficiency.
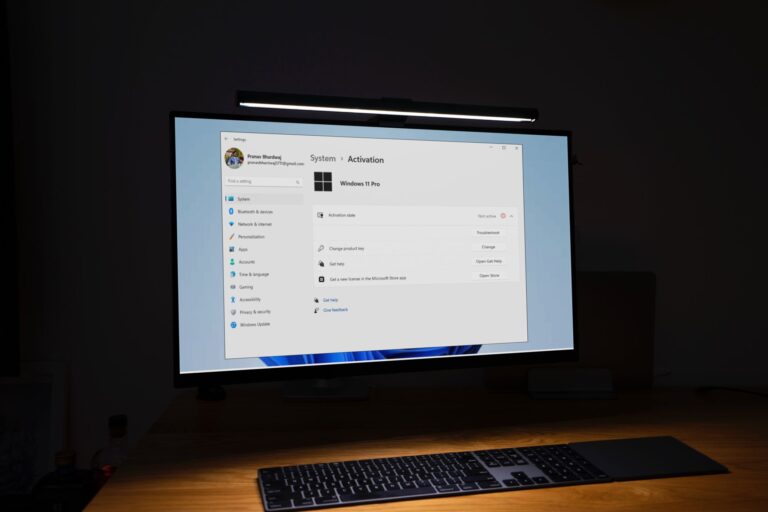
Operating a system without proper activation leads to significant customization restrictions that can hinder the overall user experience. One of the most pressing concerns relates to the handling of security updates and patches, which are critical for maintaining the integrity and safety of any digital environment.
Users who operate with a non-activated version often lack access to essential updates, leaving them exposed to various vulnerabilities. Without these regular enhancements, the system becomes susceptible to attacks from malware and other malicious entities. The absence of official patches not only compromises functionality but also increases security risks as loopholes remain unaddressed, which could have been fixed with timely updates.
Additionally, an unactivated product might restrict the ability to customize security settings or utilize advanced features designed to empower users in protecting their data effectively. These functional limits could deter individuals and organizations from implementing robust cybersecurity measures, ultimately jeopardizing sensitive information.
While some may argue that initial cost savings can be appealing, the long-term implications of not receiving timely security updates clearly outweigh this short-term benefit. The lack of support and the potential for serious breaches necessitate a well-informed decision when considering the implications of such actions.
For more detailed insights on this subject, you may refer to resources available on Microsoft’s official website: Microsoft.
Utilizing non-licensed operating systems can expose users to numerous threats, particularly in relation to malware and viruses. Unofficial versions generally come with several functional limits, making them more vulnerable to malicious software.
One critical risk associated with non-activated systems is the absence of regular updates. Updates usually address security vulnerabilities; when these are not installed, systems become easy targets for cybercriminals. Without these patches, users may unknowingly leave their data exposed to intrusions.
In addition to lacking updates, users may also encounter frequent notification prompts urging them to activate their system. These prompts can be triggers for phishing attempts, where attackers might disguise themselves as system notifications to extract personal information or install malware.
Considering these factors, the chances of encountering malware and viruses significantly increase with the use of unlicensed platforms. Users need to weigh the pros and cons of their software choices carefully and remain vigilant against online threats.
For further information on the risks of using non-activated systems, you can visit the Microsoft website: Microsoft Security.

Operating a non-activated version of a certain operating system leads to various limitations that significantly affect the user experience. One of the most noticeable aspects is the inability to receive critical updates. Updates are essential not only for security enhancements but also for improving overall system performance and stability. Without these updates, users may find their systems becoming more vulnerable to threats and less compatible with newer applications.
Additionally, users often face persistent notification prompts reminding them of the unactivated status. These interruptions can be distracting and may hinder productivity, as they require attention that could otherwise be focused on tasks at hand. Over time, this can contribute to a frustrating environment, particularly for those using their systems for professional purposes.
Functional limits are another significant drawback. Many utilities and features may be either disabled or significantly restricted. For example, advanced settings that allow for personal tailoring of the system’s appearance and behavior may not be accessible, leaving users stuck with the default configurations that may not suit their preferences or needs. This lack of customization can lead to dissatisfaction, especially for those who appreciate personalized setups.
Moreover, the absence of full access to features can restrict overall productivity. Users might miss out on functional enhancements that facilitate better performance or streamline workflows. This is especially critical in collaborative environments, where the ability to utilize the complete array of tools can directly impact team synergy and output.
In conclusion, running a non-activated system can severely limit not just the functional capacity of the operating system but also detract from the overall user satisfaction. Understanding these restrictions is vital for users considering their options and striving for optimal performance in their computing endeavors.
Operating a non-licensed operating system can lead to various legal issues and penalties. Individuals or organizations that choose to forgo activation may find themselves facing several challenges.
Furthermore, companies may face legal action if they are found utilizing unlicensed copies of operating systems. The penalties for such activities can be severe, potentially including:
On the individual level, penalties might be less extensive but still impactful. Users may be subjected to fines and an inability to access critical updates, putting their devices at risk.
In summary, the long-term implications of remaining unactivated can outweigh any short-term savings. Weighing these factors carefully is essential for making informed decisions regarding software compliance.
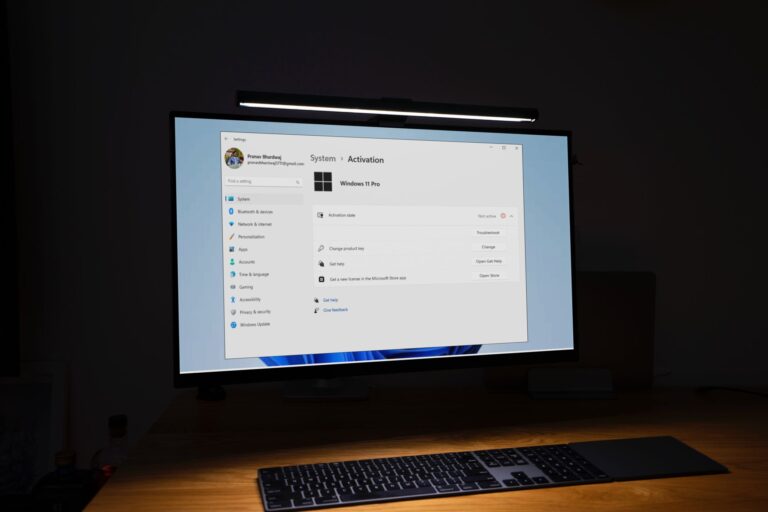
Utilizing a version of an operating system without proper activation can lead to significant hurdles, particularly when integrating third-party applications. One of the primary concerns is the presence of customization restrictions, which often limit users from modifying settings or personalizing their environment to suit their preferences.
Users may encounter functional limits that hinder the performance of various applications. Many third-party programs rely on certain system APIs and frameworks that may not operate correctly in an unlicensed context. This can lead to frustrating experiences, particularly for those who depend on specific functionalities for business or creative tasks.
Another issue arises with notification prompts. Often, unverified versions of the operating system will generate persistent alerts that disrupt workflow. Frequent interruptions can impede productivity, causing users to lose focus on essential tasks.
Furthermore, access to important updates may be restricted. Updates can provide critical security patches and new features essential for maintaining compatibility with new applications and services. Without these updates, the risk of experiencing conflicts and vulnerabilities increases, potentially exposing systems to security threats.
In summary, while there may be an allure to foregoing activation due to potential cost savings, the drawbacks related to third-party application compatibility can outweigh these benefits. Users must carefully consider these factors when deciding on software use and activation status.
Operating a non-authenticated version of a computer operating system can lead to significant performance limitations. Users may experience reduced speed and responsiveness, often because the software is not optimized for full functionality. These functional limits can manifest in sluggish application launches, delayed responses, and time-consuming operations, creating an overall frustrating experience.
Moreover, without the ability to access customization options, individuals are restricted in their capacity to tailor the operating environment to their preferences. These restrictions prevent users from fine-tuning settings or enabling features that enhance productivity, ultimately affecting their workflow and efficiency.
Updates are a crucial aspect of any software, as they often contain essential improvements and bug fixes. However, without a valid license, users may miss out on critical security patches and performance enhancements, leaving their systems vulnerable. This gap in security not only jeopardizes personal data but may also lead to malware or virus attacks, further hindering system stability.
The associated security risks can create a vicious cycle where instability leads to performance degradation, prompting users to install additional security measures, which in turn can slow down system performance even further. As illustrated in the following table, the comparison between validated and non-validated versions highlights these significant differences.
| Feature | Validated Version | Non-Validated Version |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | Optimized and fast | Slow and laggy |
| Customization | Extensive options available | Limited functionality |
| Updates | Regular updates with security patches | Infrequent updates, security risks present |
| System Stability | Stable and reliable | Prone to crashes and errors |
Analyzing these aspects reveals a clear distinction; maintaining a validated version fosters a more reliable and performant computing environment. When weighing the benefits against the drawbacks, it becomes evident that opting for an unlicensed iteration may compromise not just performance and functionality, but also security and system stability. Ultimately, users must consider the impact of their choices in order to protect their systems and enhance their overall experience.
Choosing to operate without a licensed version significantly limits access to technical assistance and updates. Official releases typically come with customer support channels, offering solutions to problems as they arise. Users without license keys often find themselves isolated, deepening their reliance on online forums and unofficial resources, which may not provide accurate or reliable guidance.
Updates are a critical aspect of maintaining optimal performance and security. Licensed versions receive frequent updates that patch vulnerabilities and introduce new features. In contrast, those who opt for unregistered systems are likely to miss out on these upgrades, exposing their systems to potential security risks. Cyber threats evolve, and the absence of patches leaves unprotected gaps that malicious entities can exploit.
Additionally, individuals operating without a legitimate version frequently encounter notification prompts urging them to activate their software. While seemingly benign, these alerts can disrupt workflow and focus. Constant reminders can hinder productivity and lead to frustration, creating an unfavorable user experience.
Functional limits imposed by unofficial usage prevent access to advanced features and integrations that could enhance overall effectiveness. This limitation holds back users who could benefit from enhancements offered to paying customers. As a result, individuals might struggle with outdated processes and capabilities, impeding their ability to perform tasks efficiently.
The decision to remain unregistered impacts not only personal productivity but also organizational reliability. Companies relying on unlicensed versions may find themselves less competitive in the marketplace due to outdated technology and lack of support. Identifying and addressing these issues early on can be critical for long-term success.
Utilizing unregistered applications raises significant concerns for organizations that must adhere to legal regulations surrounding compliance and licensing. Companies that operate without legitimate activation face functional limits that hinder essential features necessary for daily operations. For instance, access to specific tools and utilities may be restricted, affecting productivity and workflow.
Moreover, failure to register can result in irregular updates. Regular system updates are crucial for maintaining optimal performance and fixing vulnerabilities. Unactivated systems often miss out on these critical patches, leaving businesses susceptible to security risks. Cyber threats are on the rise, and outdated systems can become easy targets for malicious attacks. Statistics indicate that over 50% of data breaches occur due to unpatched vulnerabilities, highlighting the importance of updating software regularly.
In addition to security concerns, enterprises may encounter frequent notification prompts that disrupt user experience. These notifications serve as reminders of unlicensed status, which can lead to decreased morale among employees. Constant interruptions may distract from critical tasks, thereby impacting overall efficiency.
Another pressing issue relates to the legal liabilities incurred by businesses operating with non-compliant applications. Organizations risk hefty fines and legal action if discovered. Recent studies reveal that businesses face penalties ranging from thousands to millions of dollars for software licensing violations. This potential financial burden can significantly outweigh the initial savings of avoiding proper registration.
Considering these factors, the analysis presents a clear picture. While the initial allure of avoiding licensing fees might seem tempting, the long-term implications can lead to diminished productivity, elevated security concerns, and substantial financial repercussions. Organizations must evaluate the trade-offs and prioritize compliance to ensure sustainable growth and robustness in their operational practices.