Physical Address
Timertau, Pr. Respubliki 19, kv 10
Physical Address
Timertau, Pr. Respubliki 19, kv 10

Cloud subscriptions offer scalable resources, allowing companies to adjust their needs based on fluctuating demands. Unlike traditional models requiring substantial upfront investments, the subscription-based approach facilitates easier budgeting and allocation of funds. The ability to add or remove licenses effortlessly also contributes to its popularity among enterprises aiming for operational flexibility without the burden of excess expenditure.
In understanding the implications of each method, organizations can make informed decisions that align best with their operational strategies. Through this examination, we aim to clarify the potential benefits and challenges associated with each model, guiding decision-makers in selecting the solution most suitable for their unique requirements.
The distinction between cloud subscription models and on-premises software licenses is significant. The move towards a cloud-based approach provides numerous benefits, particularly with scalable resources. Companies often seek to leverage this flexibility to access virtual desktops without the need for extensive physical infrastructure.
In a cloud subscription model, businesses typically pay a monthly fee, which makes budgeting more predictable. This contrasts sharply with traditional licensing, where upfront costs may be substantial and ongoing maintenance can add hidden expenses. Cloud solutions enable organizations to adjust their resources seamlessly, scaling up or down based on demand.
Utilizing a virtual desktop solution allows employees to work from anywhere while maintaining centralized access to necessary applications and data. This is particularly advantageous for remote work arrangements, as it ensures consistency in user experience regardless of location.
Another aspect to consider is the enterprise model adopted by many cloud services. This model focuses on delivering comprehensive solutions that integrate with existing IT frameworks. Licensing arrangements, on the other hand, may require additional components to achieve similar integration, potentially complicating deployment.
Overall, the choice between these approaches depends on organizational needs, budget constraints, and future growth plans. Cloud subscriptions can provide flexibility and convenience, while traditional licenses offer ownership and control. Businesses should weigh these factors carefully when making decisions.
For further insights on this topic, you can visit the official Microsoft documentation: Microsoft Official Site.

When evaluating software procurement, organizations face a choice between multiple payment structures. Understanding the differences between a recurring monthly fee and a one-time purchase is vital for making an informed decision.
A cloud subscription typically involves a monthly fee, giving businesses access to scalable resources without the hefty initial investment. This enterprise model allows for:
Conversely, a one-time purchase results in payment upfront, offering ownership of the software. This option may appeal to organizations that prefer less ongoing financial commitment. Key points include:
Both pricing models have distinct advantages and disadvantages. Companies should assess their specific requirements, including budget constraints and growth projections, to determine which financial strategy aligns best with their operational goals.
In the modern business environment, organizations are increasingly focusing on optimizing their IT resources to meet their evolving needs. When evaluating different licensing models, scalability and flexibility play a crucial role in determining the best fit for a company’s requirements.
The enterprise model provides an appealing option for businesses looking for customizable virtual environments. This approach allows companies to adjust their scalable resources based on fluctuating demands, facilitating the addition or removal of users and features without extensive downtime or additional costs.
One of the key advantages of this model is the predictable monthly fee structure, which aids in budgeting and financial planning. Businesses can allocate funds more effectively because they know exactly what their IT expenses will be each month. This contrasts sharply with traditional purchasing methods, where costs can vary significantly according to hardware and software requirements.
Virtual desktops offer enhanced agility in resource allocation. Organizations can quickly scale up during peak times or reduce capacity when demand decreases. This dynamic adaptability enables companies to remain agile and responsive to market forces without the need for significant upfront investments.
Additionally, the option to shift resources on demand means organizations can explore new technologies or adapt processes without long-term commitments. This flexibility ensures that businesses are not tied down by rigid contracts or excessive licensing provisions, allowing them to pivot as necessary.
In summary, the focus on scalability and flexibility in licensing methods is paramount for contemporary businesses. An enterprise model not only supports dynamic resource management but also ensures financial predictability, making it an attractive solution for organizations of all sizes.
When assessing the security landscape of various computing solutions, it is crucial to differentiate between cloud-based environments and conventional installation methods. This section focuses on the protective measures associated with virtual desktops versus traditional setups.
Both types of solutions present unique security benefits. However, organizations should weigh the advantages of modern, managed services against the traditional methods to make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements.
For detailed information on security comparisons between different computing models, visit the Microsoft Security Center.
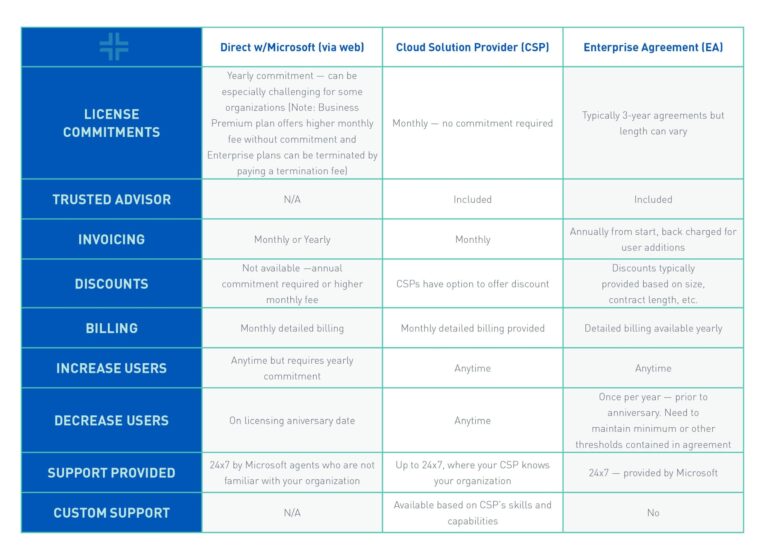
When assessing the accessibility and compatibility of different software delivery models, significant factors are involved. A pivotal distinction between cloud-based and conventional systems lies in their flexibility regarding device usage.
With a cloud subscription, users can access their workspaces from virtually any device with an internet connection. This includes laptops, tablets, and smartphones, allowing a high level of mobility. The cloud solution provides a virtual desktop experience, meaning resources are delivered online, reducing the need for extensive local hardware capabilities.
On the other hand, traditional setups often require specific system configurations tied to particular operating systems. This limits the variety of devices that can effectively run the software, leading to potentially higher costs due to necessary upgrades or specialized hardware. Additionally, achieving remote access typically requires a Virtual Private Network (VPN) or other configurations, often adding complexity to the setup process.
Another advantage of a cloud subscription model is the monthly fee structure, which allows for predictable budgeting. Organizations can scale resources according to their needs, adjusting user licenses and capabilities with ease without the upfront costs associated with traditional licenses.
In enterprise models, this flexibility becomes invaluable. Teams can rapidly expand or contract based on project demands, ensuring that the right tools are always at hand without overcommitting financially. Compatibility issues can also be minimized as updates and support are managed centrally by the provider, ensuring all users are on the same version of the software.
To summarize:
Considering these factors will help organizations determine the most effective approach for their software needs, balancing accessibility with resource management.
In today’s competitive environment, organizations need to carefully evaluate their support and maintenance strategies. The choice between a fixed payment model and a cloud subscription can significantly impact operational efficiency and resource allocation.
One of the primary benefits of a cloud subscription is the monthly fee structure. This approach offers a predictable expense model, making budgeting easier for businesses at any scale. With this system, costs remain transparent and manageable, allowing for effective financial planning.
Scalable resources also play a vital role in the contemporary enterprise model. Cloud-based services provide the flexibility to adjust resource levels based on changing demands. Businesses can increase or reduce access to applications and services without the need for significant upfront investments or long-term commitments.
Support requirements can differ based on the chosen approach. Traditional methods may require dedicated IT personnel for maintenance, updates, and troubleshooting, often resulting in unforeseen costs. Conversely, a cloud subscription typically includes integrated support, allowing businesses to focus on core operations while relying on the service provider for system upkeep.
Moreover, organizations can enjoy the advantages of regular updates and enhancements with cloud solutions, ensuring that they always have access to the latest tools and features. This reduces the risk of obsolescence and fosters innovation within the company.
Ultimately, the decision regarding support and maintenance should consider both current needs and future growth potential. By weighing the benefits of predictable costs, scalable resources, and comprehensive support systems, organizations can select the option that aligns best with their long-term objectives.
Choosing the right software procurement strategy can significantly impact your organization’s productivity and budget management. Below are several factors to consider when evaluating which model aligns best with your company’s requirements.
A recurring monthly fee can aid in forecasting expenses and ensuring adherence to budgetary constraints. For businesses with tight financial planning, this predictability allows for better cash flow management compared to hefty upfront payments often associated with conventional models.
Today’s organizations may grow or contract rapidly. Subscription-based solutions provide flexibility, enabling businesses to easily adjust their service levels according to current needs. This scalability helps prevent the waste of resources typically seen with static licensing agreements.
With an increasing trend toward remote work, having access to a virtual desktop can enhance workplace efficiency. Employees can access their projects and applications from various devices, which is particularly beneficial for organizations with distributed teams.
The enterprise model often includes additional tools and services catering to larger organizations. These may involve advanced security measures, tiered support options, and integration capabilities with existing systems, allowing for a more robust framework for managing extensive operations.
Before making a decision, assess the following elements for your organization:
Ultimately, select the approach that aligns with your organization’s long-term strategy while ensuring optimal resource allocation and financial management.
| Factor | Subscription Model | Traditional Model |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Predictability | High | Low |
| Scalability | Flexible | Rigid |
| Virtual Desktop Access | Included | Limited |
| Enterprise Features | Advanced | Basic |