Physical Address
Timertau, Pr. Respubliki 19, kv 10
Physical Address
Timertau, Pr. Respubliki 19, kv 10

The debate surrounding the permissibility of utilizing unlicensed software has sparked considerable discussion, particularly with regard to the implications of the Microsoft policy. Many users often find themselves pondering whether or not they can operate without securing a formal license. This inquiry brings forth critical considerations about the license agreement offered by the corporation and the ramifications of failing to comply with its stipulations.
Engaging with an unlicensed version of the software can lead to a myriad of complications. Users may encounter limitations that restrict their ability to access certain features, often referred to as limited functionality. These constraints are not merely inconveniences but serve as reminders that the experience provided is not in alignment with the comprehensive offerings available to licensed users.
Understanding the parameters set forth in the terms of use is imperative for anyone contemplating the adoption of software outside the official channels. These terms explicitly outline what is permissible and what constitutes a violation, thus equipping users with the necessary information to make informed choices about their software usage.
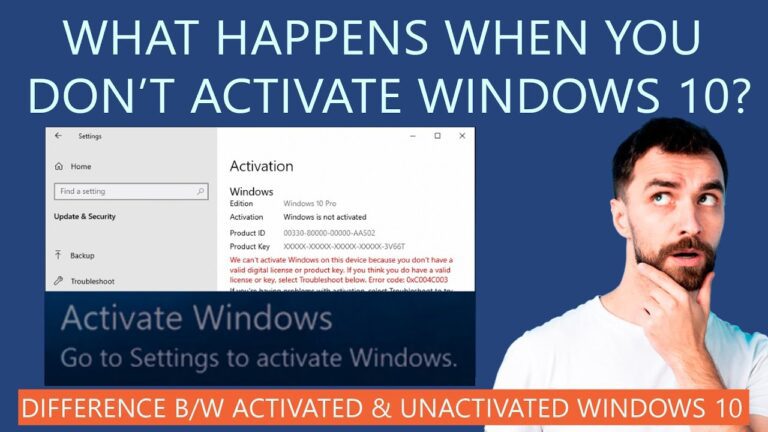
When it comes to unlicensed software, the consequences can be significant. Different countries have various laws regarding the use of unregistered operating systems; however, a common ground is provided by Microsoft’s policy. This includes the stipulation that each installation should have a valid license, reflecting a legal contract between the user and the company.
Choosing to run software without proper activation poses certain risks. These encompass legal repercussions that may lead to fines or civil actions, depending on the jurisdiction. Moreover, individuals using an unlicensed version might face limitations in terms of updates and security patches, leaving their systems vulnerable to threats.
Engaging with software not compliant with the license agreement raises ethical questions as well. Companies invest time and resources in developing and maintaining their products; therefore, utilizing their offerings without compensation undermines these efforts. Legal claims may arise if the situation escalates, putting the user at a disadvantage.
Potential consequences of operating an unauthorized version include:
Ultimately, users should weigh the benefits of legitimate software against the risks associated with unlicensed usage, while considering the ethical implications embedded in the license agreement. Establishing a clear understanding of one’s rights and responsibilities can lead to better decision-making regarding software utilization.
Opting for a non-activated version of your operating system may seem like an attractive choice, but it comes with several significant drawbacks that users should be aware of. Engaging with such software could violate the license agreement, leading to potential legal ramifications.
One of the most prominent issues is the limited functionality offered by these versions. Users may find key features disabled or restricted, which can hinder productivity. Moreover, regular updates from the developer may not be available, leaving the system vulnerable to security threats.
Additionally, utilizing unlicensed software exposes individuals to several risks. These include:
Selling non-activated software often exists in a legal gray area, conflicting with Microsoft policy. If you’re considering making a purchase, it’s crucial to seek reputable sources. You can find safe options at Where to buy license safely and Learn more about buying keys securely.
For further understanding of software licensing, refer to the Microsoft Services Agreement, which provides comprehensive information regarding the conditions and stipulations that govern the use of their products.
Many individuals consider the implications of using a system that is not properly licensed. The experience varies significantly between a fully activated setup and one lacking proper validation. Understanding these differences helps users make informed decisions.
In an activated environment, users enjoy full access to features and updates. This includes:
However, when operating in a non-validated setting, users encounter several restrictions:
According to Microsoft policy, it is crucial for users to adhere to the outlined terms of use. The license agreement stipulates that to fully benefit from the system, activation is necessary. Users should consider these regulations to avoid potential complications connected to non-compliance.
In conclusion, while a non-validated setup may appear to be an option, the drawbacks significantly outweigh any immediate benefits. The enhanced user experience in a properly licensed environment plays a vital role in maintaining system security and performance.
Microsoft has established clear guidelines regarding software licensing, emphasizing the importance of adhering to the license agreement associated with its operating systems. Understanding these policies is crucial for users and organizations alike.
The core elements of Microsoft’s stance on compliance include:
To maintain a legitimate and fully operational system, it is essential to activate the operating system according to Microsoft’s regulations. This ensures that all features are accessible and that users remain in compliance with the outlined agreements.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| License Agreement | Document outlining user rights and responsibilities. |
| Microsoft Policy | Framework for compliance and enforcement of licensing. |
| Terms of Use | Conditions for acceptable usage of the software. |
| Limited Functionality | Consequences of non-activation, restricting software capabilities. |
Understanding these principles is vital for all users to ensure they are utilizing their software in accordance with Microsoft’s expectations and maintaining the integrity of their operating system.
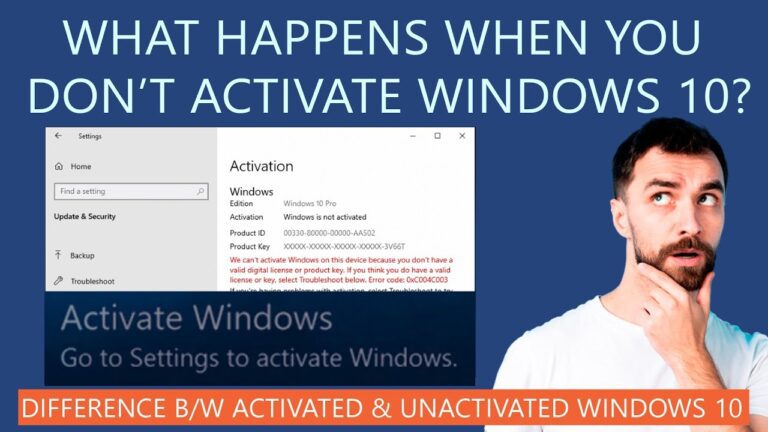
There are several ways to transition to a compliant computing experience without settling for a system that operates with limitations due to non-activation. Below are options that fit within the boundaries of Microsoft policy and its terms of use.
Choosing non-compliant methods carries significant risks, including potential data loss or security vulnerabilities. Opting for legitimate solutions ensures not only adherence to legal standards but also security and access to ongoing updates, minimizing the drawbacks associated with limited functionality.
For more in-depth insights into compliance and software use, refer to the official Microsoft website.