Physical Address
Timertau, Pr. Respubliki 19, kv 10
Physical Address
Timertau, Pr. Respubliki 19, kv 10

Another noteworthy factor is the limitations on customization options imposed by non-activated versions. Users often find themselves constrained in personalizing their systems to fit their needs or preferences. These restrictions can frustrate those who desire a tailored experience, leading to a sense of dissatisfaction and impacting productivity.
Security risks are an ever-present concern in the realm of non-activated software. The absence of official updates means that potential threats linger longer without remediation. Unaddressed vulnerabilities can create a fertile ground for cyber threats. Additionally, the frequent notification prompts that indicate the software’s unactivated status can disrupt workflows and divert attention from tasks at hand, compounding the drawbacks of the overall experience.

Utilizing a non-activated version of Windows can lead to various legal challenges for users. Primarily, the software may not adhere to licensing agreements, which can result in severe consequences.
Many users encounter functional limits, restricting access to critical features. Typically, unregistered copies will not receive updates or support from the software provider. This can hinder performance and functionality, making it challenging for users to operate efficiently.
Customization restrictions also come into play. Unactivated versions often prevent modifications to system settings or personalization options. This limitation can impact user experience, especially for those who have specific needs or preferences for their operating environment.
| Aspect | Activated | Unactivated |
|---|---|---|
| Functional Limitations | Full functionality | Restricted access |
| Customization | Fully customizable | Limited options |
| Notifications | No prompts | Frequent notification prompts |
| Security | Regular updates and support | Increased security risks |
Frequent notification prompts are another major concern. Unactivated versions will constantly remind users of the need to activate. This can be intrusive and detracts from productivity, as users are forced to deal with these interruptions regularly.
Furthermore, running software that is not properly authenticated raises significant security risks. Unverified programs may contain vulnerabilities that expose the system to cyber threats, potentially compromising sensitive information. Without proper updates and patches, users remain vulnerable to attacks or malware, which can lead to additional legal issues if user data is exposed or stolen.
In conclusion, while using an unlicensed operating system may seem cost-effective in the short term, the long-term implications can lead to legal troubles, reduced functionality, and compromised security, making it an unwise choice for users who seek reliability and peace of mind.
The absence of activation for certain operating systems can significantly influence the manner in which updates and security patches are managed. Those who opt for unlicensed editions often encounter severe limitations in receiving timely and critical updates. This can expose users to various security risks, as outdated software may harbor vulnerabilities that are easily exploitable by malicious actors.
Furthermore, users may face customization restrictions that prevent them from fully optimizing their systems for security. The lack of access to official updates also means that recent threats may not be addressed, leaving systems susceptible to attacks. Notifications regarding available updates frequently pop up, which may annoy users; however, these alerts are essential for maintaining system integrity.
As security landscapes evolve, the importance of timely updates cannot be understated. Official versions of software not only provide regular patches but also ensure compatibility with the latest security protocols. In contrast, those with an unactivated version might find themselves without support, missing out on enhancements that could adequately protect their systems from emerging threats. Consequently, opting for such editions can lead to significant long-term ramifications regarding system reliability and personal data security.
For detailed information on Microsoft software updates and security practices, you can visit the official Microsoft website: Microsoft Security.
One of the most significant consequences of utilizing an unlicensed version of an operating system is the limitation in features. Users may experience functional limits on essential tools and applications. Certain functionalities, such as advanced security measures and enhanced performance optimizations, are often reserved for fully activated versions. This restriction can hinder productivity and overall user satisfaction.
Moreover, the lack of regular updates is a critical concern. Users without an appropriate license may miss out on vital security patches and system improvements. These updates are designed to enhance both the safety and performance of software, and their absence can lead to increased vulnerabilities. As a result, the potential for exploitation by malicious entities grows significantly.
Another notable drawback is the prevalence of customization restrictions. Unactivated versions typically offer limited options for personalizing the user experience. This can include restricted access to themes, desktop backgrounds, and other interface modifications that many users find essential for a tailored computing environment.
Additionally, the overall user experience may be diminished, as some features might be disabled altogether. This can lead to frustration among individuals who rely on specific capabilities for their daily tasks. Without full access, users cannot take full advantage of the software’s capabilities, ultimately affecting their workflow and efficiency.
In summary, those who choose to operate without a valid license face significant challenges in terms of security risks, limited functionality, lack of updates, and customization restrictions. For a reliable and comprehensive experience, obtaining proper activation is advisable. For further reading on this topic, visit Microsoft’s official website.
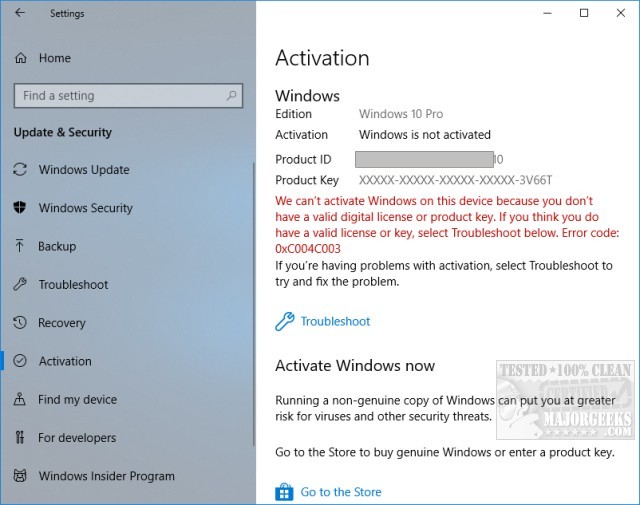
Utilizing a non-genuine operating system often leads to increased exposure to malicious programs. These variants are typically designed to exploit vulnerabilities present in outdated or unverified versions of software. The lack of regular updates magnifies this threat, as users miss critical security enhancements that protect against known exploits.
Statistics show that users operating on unverified software face a significantly higher risk of infection compared to those who maintain authentic systems. According to cybersecurity reports, individuals using non-genuine systems are approximately 60% more likely to encounter malware incidents.
In conclusion, opting for a counterfeit operating system introduces serious security challenges and performance limitations. Regular updates and genuine software licenses not only enhance the overall user experience but also provide critical safeguards against the complex array of cyber threats. Thus, maintaining authenticity proves to be a wise investment in both security and functionality.

Operating systems that remain unregistered can present serious challenges related to compatibility with various third-party applications. These programs often require specific updates to function seamlessly, and the lack of activation can hinder access to crucial patches and enhancements. As a result, users may experience instability or reduced performance in their applications, ultimately affecting their overall productivity.
Additionally, unactivated systems can lead to frequent notification prompts that disrupt workflow. These interruptions are designed to encourage users to activate their software, but they can also impede the proper functioning of other applications. The continuous reminders can distract users, making it difficult to focus on important tasks.
Another significant aspect is the security risks associated with running non-activated operating systems. Many applications depend on the underlying system’s security features to operate safely. Without official updates, vulnerabilities may remain unaddressed, exposing the entire system to potential attacks. Consequently, third-party software could become an easy target for malware or other cyber threats, increasing the likelihood of data breaches.
Customization restrictions can also arise when using an unregistered system. Certain applications may require specific configurations that are incompatible with an unactivated environment. This limitation can prevent users from tailoring their software to meet their individual needs, inhibiting an optimal user experience.
To conclude, while operating an unregistered system may seem viable, the compatibility hurdles with third-party applications, ongoing notifications, security vulnerabilities, and limitations in customization can significantly impact users. Careful consideration of these factors is essential for making informed decisions regarding software use.
Access to technical assistance becomes increasingly limited for individuals relying on non-validated systems. These platforms often lack eligibility for updates that introduce enhancements and security patches, leaving users vulnerable to emerging threats. Without timely improvements, the reliability of such systems diminishes, potentially resulting in more frequent issues requiring resolution.
Another significant concern lies in customization restrictions. Users seeking to modify their setup or integrate specific features may encounter obstacles. This limitation can severely hinder personal efficiency and reduce the overall user experience, as many tailored functionalities are often reserved for validated versions.
Moreover, security risks escalate without adequate support from the original developers. Trouble arising from malware or compatibility issues may not have straightforward solutions, as unverified software versions might not receive necessary patches. The absence of official guidance during these stressful situations adds to user frustration and may lead to long-term implications for data protection.
Functional limits are another drawback deserving attention. Users may find that specific software applications operate at a diminished capacity compared to fully licensed counterparts. Essential tools and features may remain inaccessible, thus restricting the potential use of the system and impairing productivity levels.
In conclusion, reliance on non-validated platforms poses several challenges concerning technical assistance, ultimately affecting the user’s experience, security, and functional capabilities. Making informed choices about software status is critical for maintaining operational effectiveness and safeguarding sensitive data.
Utilizing non-activated platforms can lead to various performance difficulties that may affect the user experience. Below are some critical factors to consider:
Comparison of activated and non-activated systems highlights these performance challenges significantly. Users can expect smoother operation, continuous updates, and enhanced security in legitimate versions. Evaluating these differences enables individuals to make a well-informed choice regarding their software usage, balancing functionality with potential risks.