Physical Address
Timertau, Pr. Respubliki 19, kv 10
Physical Address
Timertau, Pr. Respubliki 19, kv 10

In today’s dynamic market, choosing the right operating system for businesses is paramount. Organizations seek to maximize business productivity while ensuring robust security enhancements. Understanding the different levels of available options can greatly influence a company’s operational success and cost management.
This article aims to outline the various enterprise tools offered across different versions of the operating systems tailored for professional use. Each version brings a distinct set of capabilities that cater to specific business needs, from cost considerations to specialized functionalities.
By exploring the pricing structure and the unique functionalities available in each tier, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their strategic goals. Knowing the differences in features not only aids in budgeting but also enhances overall workplace efficiency and security measures.
User Account Control (UAC) plays a significant role in maintaining security within operating systems. It regulates permissions and helps prevent unauthorized changes. The variations in UAC implementations between editions can impact IT management and security protocols for organizations.
The approach to User Account Control differs in terms of configuration options and granular control:
| Edition | UAC Configuration Options | Management Capabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Version | Basic UAC settings | Limited control |
| Advanced Version | Enhanced options allowing for customization | Advanced management tools for IT |
For administrative tasks and system changes, the more advanced version allows for a stringent approach to user permissions. IT managers appreciate these capabilities for ensuring compliance with organizational policies.
With increased UAC control comes improved security enhancements, capable of defending against unauthorized access:
– Fine-tuned notification prompts
– User role segmentation
– Automatic elevation of privileges for trusted applications
The advanced configuration fosters a safer environment, mitigating risks associated with malware and unauthorized changes.
The financial aspect of each edition also plays a role in decision-making for organizations:
– Standard Version: Generally lower cost, suitable for small businesses.
– Advanced Version: Higher pricing reflects the expanded scope of enterprise tools and security features.
Organizations must weigh the initial costs against potential security gains and IT management efficiencies.
Recognizing the distinctions in User Account Control between these editions is imperative for senior management and IT departments. By opting for the version that aligns best with their security needs and management requirements, organizations can enhance their operational integrity while providing protection against threats.
When analyzing the advantages available in different operating systems for business environments, two critical components stand out: BitLocker and Windows Defender. These tools offer significant security enhancements that can bolster organizational defenses while improving business productivity.
BitLocker: This is a disk encryption feature that safeguards data by encrypting entire volumes. Here are some key aspects:
The availability of BitLocker presents an opportunity for organizations to secure their data comprehensively. Its implementation can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and leaks.
Windows Defender: This built-in security solution is designed to protect devices against a wide range of threats. Its features include:
With Windows Defender, businesses can confidently maintain their security posture without incurring additional costs associated with third-party antivirus solutions, thus impacting pricing strategies positively.
In conclusion, the integration of BitLocker and Windows Defender into organizational practices not only fortifies security but also contributes to improved productivity and operational efficiency. By utilizing these tools, companies can protect their digital assets while ensuring smooth business processes.
For more detailed information on these security tools, you can visit the official Microsoft security page: Microsoft Security for Business.

Virtualization has become a key component in enhancing business productivity and optimizing IT management. One of the prominent tools available for virtualization is Hyper-V, which offers various functions tailored for different organizational needs. This section examines the comparative capabilities of Hyper-V in two distinct editions designed for professional environments.
The virtualization functionalities provided by Hyper-V cater to both editions, but they differ in depth and range:
IT management tools vary significantly, impacting how organizations approach virtualization:
Budget is always a consideration for organizations when choosing between editions:
Choosing the right edition with Hyper-V capabilities hinges on an organization’s size, goals, and virtualization requirements. The more feature-rich variant is designed for those needing robust enterprise tools that enhance efficiency in IT management. In contrast, smaller businesses may opt for the professional edition to meet foundational virtualization needs without excessive investment. Understanding these distinctions can enable organizations to align their tech infrastructure with strategic business objectives.
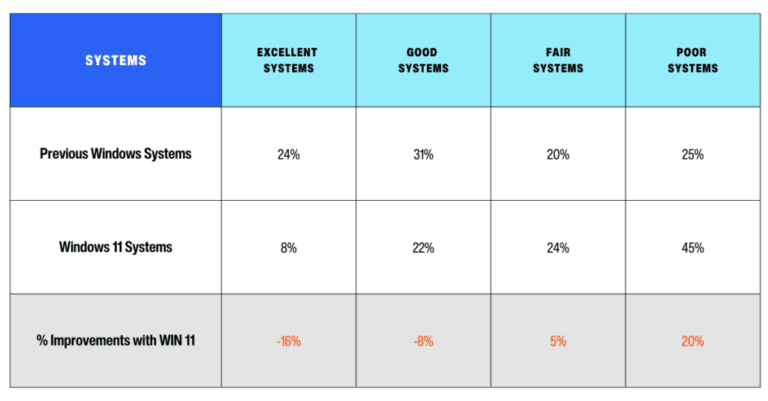
Effective IT management is paramount for businesses striving to maintain productivity and security across their networks. One of the vital tools in achieving this is Group Policy Management, which allows organizations to enforce specific configurations on devices and applications consistently.
With this system, administrators can define various settings, such as password policies, software installation, and user permissions, ensuring compliance with organizational standards. Here’s how organizations benefit from this approach:
For instance, an organization may set up a policy that automatically installs required software on all user devices during startup. This not only saves time but ensures that all employees are using the same necessary tools to perform their jobs efficiently.
Additionally, organizations can tailor policies based on user roles, enabling flexibility while maintaining security. This capability supports diverse environments where various teams may have different needs without compromising overall governance.
Overall, utilizing Group Policy Management enables businesses to address IT management challenges effectively, ensuring both security and productivity remain at the forefront of organizational goals.
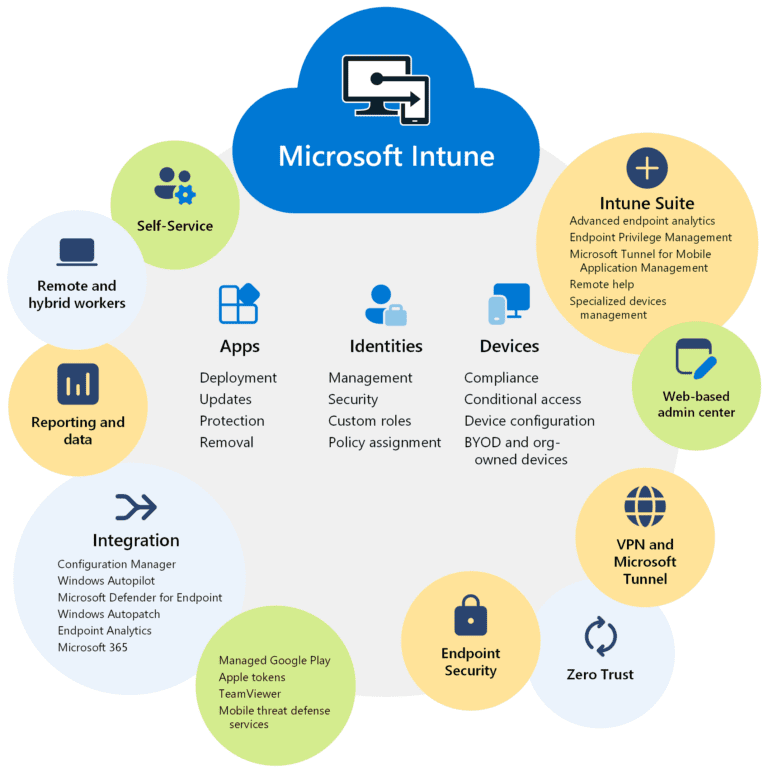
In large organizations, efficient deployment and update management are critical to maintaining business productivity and optimizing IT management. Different solutions cater to varying needs, with specific pricing structures and features designed for different types of users. Below, we examine some key tools available for this purpose, highlighting their offerings.
When evaluating these tools, organizations should consider:
Each tool provides unique advantages that can greatly enhance the deployment and update management processes within large organizations. Selecting the right solution will depend on the specific needs, size, and IT strategy of the organization.
For more detailed information and resources about these tools, visit the official Microsoft website: Microsoft.